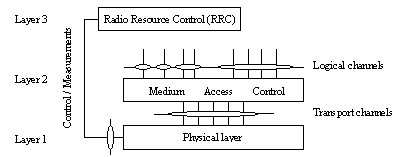
Transport channels provide for information transfer between the physical layer and the medium access control (MAC) layer in the three layer structure illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Layers
The following downlink transport channels are defined:
Broadcast channel (BCH)
Paging channel (PCH)
Downlink shared channel (DL-SCH)
Multicast channel (MCH)
Downlink transport channels are mapped to downlink physical channels as shown in Figure 2.
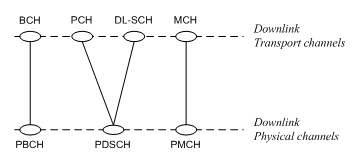
Figure 2. Downlink Transport Channel Mapping
The broadcast channel processes incoming data as follows:
Adds the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error detection
Adds tail-biting convolutional encoding
Performs rate matching
Performs channel interleaving
The downlink shared channel, paging channel, and multicast channel process the incoming data as follows:
Adds the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error detection
Performs code block segmentation
Adds turbo encoding
Performs rate matching
Performs code block concatenation